equals方法
Object类
1.默认Object类的equals方法,效果与 == 效果是相同的,必须是同一个对象 返回值为true,用来判断对象与参数对象是否相等。
2.当equals方法重写时,一般都伴随hashCode方法的重写,达到相对的对象有相等的哈希码值的需求。
代码
package com.demo;
import java.util.Objects;
public class Equals方法的使用 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student s = new Student("张三" , 18);
Student s1 = new Student("张三1" , 18);
// System.out.println(s.equals(s1));
// System.out.println(s.equals(null));
// System.out.println(s.equals(s));
A a = new A();
System.out.println(s.equals(a));
}
}
class A{}
class Student{
String name;
int age;
/*@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
Student student = (Student) o;
if (age != student.age) return false;
return name != null ? name.equals(student.name) : student.name == null;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
int result = name != null ? name.hashCode() : 0;
result = 31 * result + age;
return result; }
*/
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
Student student = (Student) o;
return age == student.age &&
Objects.equals(name, student.name);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(name, age);
}
/**
① 判断参数对象是否为null
② 判断参数对象与对象 是否为同一个
③ 判断参数对象与对象的数据类型是否相同
④ 判断需求的属性是否相同
*/
/* @Override
public boolean equals(Object st){
//判断是否为null
if(st == null){
return false;
}
//判断对象与参数对象是否为同一个对象
if(this == st){
return true;
}
//判断是否是同一个数据类型 getClass() ?
if( !(st instanceof Student)){
return false;
}
//向下转型
Student obj = (Student) st;
//判断对象与参数的属性值完全相同 认为同一个对象
//由于字符串是对象,需要通过equals方法来进行判断
return this.name.equals(obj.name) && this.age == obj.age;
}*/
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
public Student() {
}
public Student(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
}
String
概述
String类是一个值不可改变的常量。可以共享的。字面值"abc"的都是该类的对象。
底层: 字符数组。
例如:
String s = "abc"
总结:理解
对于没有new的,相当于在方法区的字符串常量池中创建对象,并且只创建一份。共享。
对于有new操作的,相当于在堆中创建一个新的对象,该对象中包含的字符序列从字符串常量池中来。
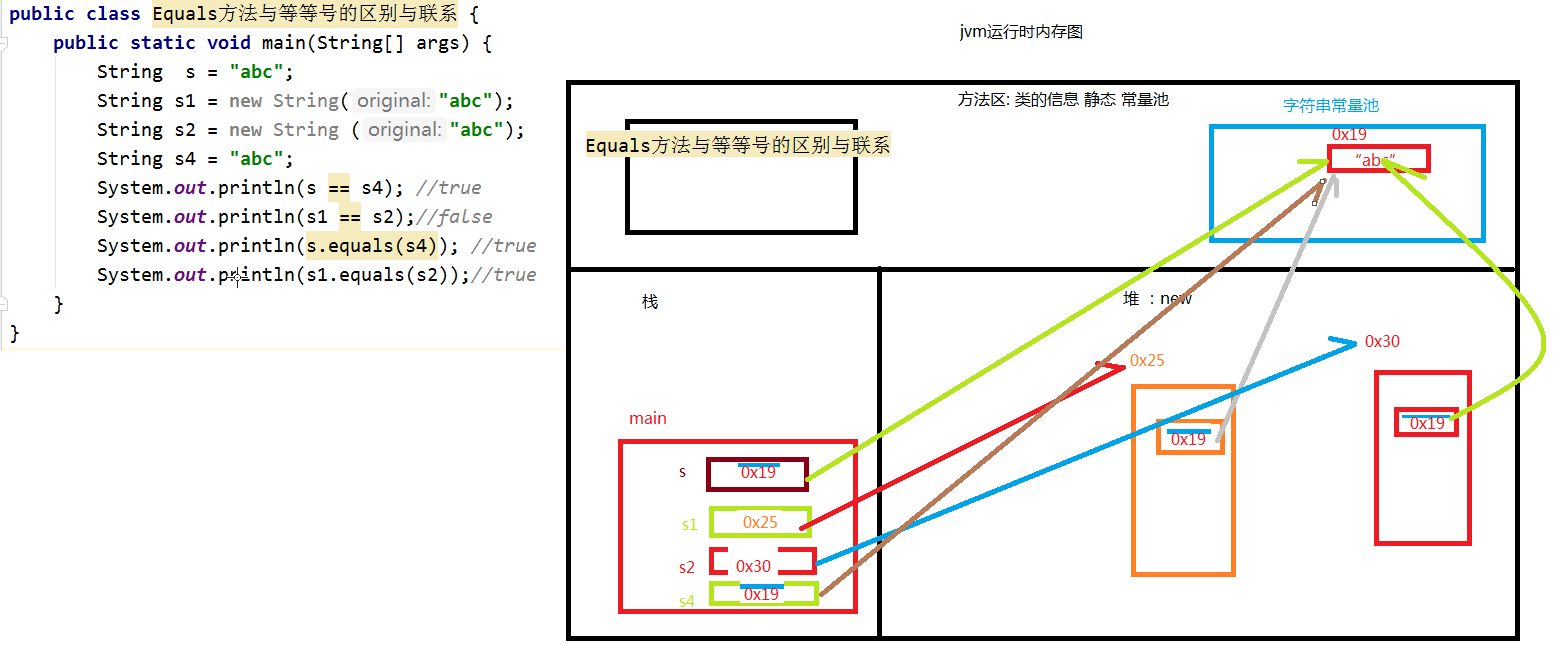
代码
package com.demo;
/**
1.(***)equals与==的区别:
① == 用来判断数值是否相同,对于基本数据类型来说,判断的是数值,对于引用数据类型,判断的 是对象的地址值是否相同。
equals方法只能判断对象是否相同,不能判断基本数据类型。
② 如果想根据需求进行判断,只能通过重写equals方法来实现。
③ 对于Object类的equals方法在没有重写的情况下,效果与== 相同。
*/
public class Equals方法与等等号的区别与联系 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = "abc";
String s1 = new String("abc");
String s2 = new String ("abc");
String s4 = "abc";
System.out.println(s == s4); //true
System.out.println(s1 == s2);//false
System.out.println(s.equals(s4)); //true
System.out.println(s1.equals(s2));//true
}
}
字符串对象创建的细节问题
对于字符串的拼接形式,如果都是字符串常量,在编译时,直接计算,这种现象称为字符串的编译器优化。
代码
package com.demo;
/**
1.字符串对象创建的细节问题:
对于字符串的拼接形式,如果都是字符串常量,在编译时,直接计算,这种现象称为字符串的编译器优化。
*/
public class 字符串对象创建的细节问题 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
T.fun();
}
}
class T{
public static void fun(){
String s = "abc";
//对于字符串的拼接形式,如果都是字符串常量,在编译时,直接计算,这种现象称为字符串的编译器优化。
String s1 = "a"+"b"+"c";
String s2 = "ab"; String
s3 = s2 + "c";
System.out.println(s == s1);//true
System.out.println( s == s3);//false
}
}
字符串常用方法一
1.charAt(int index) 返回索引位置的字符
2.compareTo(String anotherString) 按字典顺序比较两个字符串。
存在字符序列不同: 对象的unicode码- 参数的unicode码
① >0 对象在参数之后
② <0 对象在参数之前
③ =0 对象与参数相等
字符序列相同,长度不同:对象的长度-参数的长度
3.contains(CharSequence s) 判断包含
4.endsWith(String suffix)/startsWith(String prefix) 后缀/前缀
5.equals(Object anObject) 对象与参数字符序列相同,返回true 判断对象与参数字符串是否相等。
1》 equalsIgnoreCase(String anotherString) 忽略大小写。
6.getBytes(charset) 将字符串转换成字节数组。
代码
package com.demo;
import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class 字符串常用方法 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws UnsupportedEncodingException {
// 1.charAt(int index) 返回索引位置的字符
// System.out.println("abcdef".charAt(3));
// 2.compareTo(String anotherString) 按字典顺序比较两个字符串。
// System.out.println("abc".compareTo("ab"));
// System.out.println("a".compareTo("A"));
// System.out.println("a".compareToIgnoreCase("A"));
//concat(String str) 拼接
// System.out.println("abc".concat("hello"));
// 3.contains(CharSequence s) 判断包含
// System.out.println("abc".contains("ab"));
// 4.endsWith(String suffix)/startsWith(String prefix) 后缀/前缀
// System.out.println("abc.txt".endsWith("txt"));
//查找姓张的学生
String[] names = {"张三","李思","王张五","马六","张龙","李元芳"};
/*for (int i = 0; i < names.length; i++) {
if (names[i].startsWith("张")){
System.out.println(names[i]);
}
}*/
// equalsIgnoreCase(String anotherString)
/* System.out.println("aBc".equals("abc"));
System.out.println("aBc".equalsIgnoreCase("abc"));*/
// 6.getBytes() 将字符串转换成字节数组。
String s5 = "今天天气真好";
//强制类型转换无法实现字符串转字节数组
//中文gbk 两个字节一个中文
byte[] bt = s5.getBytes("GBK");
//utf-8 三个字节表示一个中文
byte[] bt1 = s5.getBytes("utf-8");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(bt));
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(bt1));
}
}
字符串常用方法二
1.isEmpty() 判断是否为空串
2.length() 字符串的长度
注意:
数组中的length是属性,不带()
字符串的length是方法,带().
3.replace(CharSequence target, CharSequence replacement) 替换所有
4.split(String regex) 根据参数拆分字符串为字符串数组
注意:
如果使用转义\ ,两个表示一个\ ,如果做拆分,4个表示两个。
代码
package com.demo;
public class String类常用方法一 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1.isEmpty() 判断是否为空串
// System.out.println("ab".isEmpty());
// lastIndexOf(String str) 用法同indexOf 返回参数字符串在字符串对象中最后一次 出现的索引值
// System.out.println("01234567823".lastIndexOf("23"));
// 2.length() 字符串的长度
int[] arr = {1,2,3,4,5};
// arr.length
// System.out.println("abc".length());
// 3.replace(CharSequence target, CharSequence replacement) 替换
// System.out.println("01234523".replace("23", "我"));
//敏感词过滤
// System.out.println("xxsadfaxxlsdljslfs".replace("x", "**"));
// 4.split(String regex) 根据参数拆分字符串为字符串数组
// String s1 = "a-b-c";
// String[] arr1 = s1.split("-");
/* String s2 ="a b c";
String[] arr1 = s2.split(" ");*/
String s3 = "a\\b\\c";
// 如果使用转义\ ,两个表示一个\ ,如果做拆分,4个表示两个。
String[] arr1 = s3.split("\\\\");
for (int i = 0; i < arr1.length; i++) {
System.out.println(arr1[i]);
}
}
}
字符串常用方法三
1.substring(int beginIndex, int endIndex) 截子串
注意:
如果只有一个参数,表示从该位置截取到末尾,如果还有第二个参数,表示从第一个参数
开始截取,到第二个索引位置-1处结束。
2.toCharArray() 字符串转字符数组
\3. valueOf(Object obj) 返回对象的字符串表示形式
代码
package com.demo;
public class String类常用方法二 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// substring(int beginIndex, int endIndex)
// System.out.println("0123456".substring(1,4));
// 2.toCharArray() 字符串转字符数组
/*String s = "abcdef";
char[] cs = s.toCharArray();
for (int i = 0; i < cs.length; i++) {
System.out.println(cs[i]);
}*/
// toLowerCase()/toUpperCase() 转小/大写
/*System.out.println("abBcD".toLowerCase());
System.out.println("abBcD".toUpperCase());*/
//toString() 转换成字符串
String s2 = new String("abc");
// System.out.println(s2.toString());
//trim() 返回字符串的副本,忽略前导空白和尾部空白。
String s3 = " a bc ";
/* System.out.println("============"+s3+"=============");
System.out.println("============"+s3.trim()+"=============");*/
// 3. valueOf(Object obj) 返回对象的字符串表示形式
System.out.println(String.valueOf("abc"));
}
}
StringBuffer 与StringBuilder
StringBuffer
概括
线程安全的可变字符序列,类似于字符串的一个字符串缓冲区。
缓冲区:
① 有富余容量
② 作为临时存储区
构造方法
1.StringBuffer构造方法:
① StringBuffer() 不带字符的字符串缓冲区,初始容量为16
② StringBuffer(int capacity) 指名初始容量
③ StringBuffer(String str) 初始容量为16+字符串长度
常用方法一
1.常用方法:
① capacity() 容量
②length()返回长度(字符数)。
③ append(Object obj) 追到到末尾
④ delete(int start, int end)/deleteCharAt(int index) 删除
注意:
[start,end) 取不到end的值为end-1
对于字符串 ,一般都是副本,是新的字符串对象,而对于字符串缓冲区来说,基本都是同一个。
代码
package com.demo;
public class StringBuffer类 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
// System.out.println(sb.capacity());
// System.out.println(sb.length());
//链式调用
sb.append("abc").append(true).append(13).append(12.3).append(1231);
//System.out.println("=========================");
// System.out.println(sb.capacity());
// System.out.println(sb.length());
// System.out.println("====================");
StringBuffer sb1 = new StringBuffer("abc");
// System.out.println(sb1.capacity());
// ④ delete(int start, int end)/deleteCharAt(int index) 删除
StringBuffer sb2 = new StringBuffer("0123456789");
// System.out.println(sb2.delete(1, 4));
// System.out.println(sb2.deleteCharAt(3));
// StringBuffer sb3 = sb2.append("345");
String ss = new String(sb2);
String ss1 = ss.concat("abc");
System.out.println(ss == ss1);
}
}
常用方法二
1.insert(int offset, Object obj) 插入
2.reverse() 反转
判断对称字符串:
abcba ==> abcba
3.toString() 转字符串
4.crud :增删改查
代码
package com.demo;
public class StringBuffer类常用方法 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = "0123456789";
StringBuffer sb1 = new StringBuffer(s);
// 1.insert(int offset, Object obj) 插入
// sb1.insert(2, "我");
// replace(int start, int end, String str) 替换 半开半闭区间 [start,end)
// System.out.println(sb1.replace(1, 4, "我们"));
// 2.reverse() 反转
// sb1.reverse();
// setCharAt(int index, char ch)
// sb1.setCharAt(1, '我');
// System.out.println( sb1);
// String与StringBuffer不是同一个类的对象
System.out.println( s.equals(sb1.toString()));
}
}
String与StringBuffer的区别
区别
1.StringBuffer在操作字符串本身时,速度比String要快,建议操作字符串本身时,用StringBuffer。
2.equals方法,Stringbuffer本身没有重写equals方法,使用的继承的Object类的equals方法,而String重写了,只要字符序列相同,就是true。
代码
package com.demo;
public class String与StringBuffer之间的区别 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = "";
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
// s += i;
sb.append(i);
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(end - start);
}
}
StringBuilder
区别
StringBuilder线程不安全的,但是执行速度比StringBuffer快。
System
概括
系统类:
有标准输入、标准输出和错误输出流。
标准输入in
标准输出out
错误输出流 err
常用方法
① currentTimeMillis() 返回当前时间的毫秒值
② exit(0) 退出jvm ,非0表示异常退出。
③ gc() 用于垃圾回收的方法。
代码
package com.demo;
import java.util.*;
/**1.属性
(***)标准输入 in
标准输出 out
错误输出流 err
2.常用方法
① currentTimeMillis() 返回当前时间的毫秒值
② exit(0) 退出jvm ,非0表示异常退出。
③ gc() 用于垃圾回收的方法。
*/
public class System类 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/* System.out.println("=================1");
System.out.println("=================2");
System.err.println("=================3");
System.out.println("=================4");
System.out.println("=================5");
System.out.println("=================6");*/
// arraycopy(Object src, int srcPos,
// Object dest, int destPos, int length) 快速数组复制。
/*
src - 源数组。
srcPos - 源数组中的起始位置。
dest - 目标数组。
destPos - 目标数据中的起始位置。
length - 要复制的数组元素的数量。
*/
/* int[] arr = {0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7};
int[] brr = new int[arr.length];
System.arraycopy(arr, 1, brr, 3, 5);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(brr));*/
// ① currentTimeMillis() 返回当前时间的毫秒值
// 从计算机历元 即1970年1月1日0时0分0秒开始计算
// System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis());
// ② exit(0) 退出jvm ,非0表示异常退出。
/*for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
if (i==3){
System.exit(0);
}
System.out.println(i);
}
System.out.println("==================");*/
// ③ gc() 用于垃圾回收的方法。
/* Person p = new Person();
p = null;
System.gc();*/
// getProperties() 系统属性
Properties prp = System.getProperties();
Set<Map.Entry<Object, Object>> set = prp.entrySet();
Iterator<Map.Entry<Object, Object>> it = set.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()){
Map.Entry<Object, Object> entry = it.next();
System.out.println(entry.getKey() + "===>"+ entry.getValue());
}
}
}
class Person{
@Override
protected void finalize() throws Throwable {
System.out.println("对象被垃圾回收了。。。。。");
}
}
Math类
概括
Math 类包含用于执行基本数学运算的方法
常用方法
① double ceil(double a) 向上取整 返回值为double
② double floor(double a) 向下取整 返回值为double
③ long round(double a) 四舍五入 返回值long类型
④ pow(double a, double b) 返回第一个参数的第二个参数次幂
⑤ random() 返回值 [0.0,1.0) 随机数
代码
package com.demo;
public class Math类 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//圆周率 Math.PI
// System.out.println(Math.PI);
//区别
/*System.out.println(Math.ceil(12.3));
System.out.println(Math.floor(12.3));
System.out.println(Math.round(12.3));
System.out.println("============");
System.out.println(Math.ceil(12.5));
System.out.println(Math.floor(12.5));
System.out.println(Math.round(12.5));*/
// ④ pow(double a, double b) 返回第一个参数的第二个参数次幂
// System.out.println(Math.pow(2 , 10));
// ⑤ random() 返回值 [0.0,1.0) 随机数
// System.out.println( Math.round(Math.random()*100));
}
}
包装类
概括
包装类:
1.引入:对基本数据类型进行功能的增强。
2.包装类中存放了一个基本数据类型。
基本数据类型 包装类
byte Byte
short Short
int ------》 Integer
long Long
float Float
double Double
char --------》 Character
boolean Boolean
3.以Integer类为例:
① 构造方法:
Integer(int/String) 字符串转Integer类型
② 常用方法:
1》 xxxValue() xxx表示基本数据类型。类型转换 。xxx表示什么返回值就是什么。
2》 parseInt(String s) 取整
3》 valueOf(String s) 字符串转换成Integer
4.装箱 与 拆箱:
① 装箱 : 基本数据类型转变成包装类。
② 拆箱: 包装类转变成基本数据类型。
1.5jdk之后,自动拆箱与装箱,基本数据类型与包装类之间不用调用方法 可以直接转换。
代码
package com.demo;
public class 包装类 { public static void main(String[] args) {
// 求int类型的最大值 /小
/*System.out.println(Integer.MAX_VALUE);
System.out.println(Integer.MIN_VALUE);*/
// Integer(int/String)
/*Integer t = new Integer("abc");
System.out.println(t );*/
Integer i1 = new Integer(12);
// 自动拆箱与装箱 1.5jdk
// int i = i1.intValue();
int i = i1;
double m = i1; //拆箱
Integer i2 = 13;//装箱
//toBinaryString(int i) 二进制 toHexString(int i) 十六进制 toOctalString(int i) 八进制
// System.out.println(Integer.toBinaryString(3));
// System.out.println(Integer.toHexString("abc".hashCode()));
}
}
Character类
常用方法:
①isDigit(char ch)判断是否为数字
② isLetter(char ch) 判断是否为字母
注意:
中文也认为是字母
③ isLetterOrDigit(int codePoint) 判断是否为字母或数字。
代码
package com.demo;
public class Character类 {
public static void main(String[] args)
// System.out.println(Character.isDigit('1'));
// System.out.println(Character.isLetter('总'));
}
}
BigInteger类
1.不可变的任意精度的整数
2.构造方法:
BigInteger(String val)
3.常用方法:
1》 加 add(BigInteger val)
2》 减 subtract(BigInteger val)
3》 乘 multiply(BigInteger val)
4》 除 divide(BigInteger val)
代码
package com.demo;
import java.math.BigInteger;
public class BigInteger类 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// long l = 11111111111111111111l;
//创建对象
BigInteger big = new
BigInteger("11111111111111111111");
BigInteger big1 = new BigInteger("11");
System.out.println(big.add(big1));
System.out.println(big.subtract(big1));
System.out.println(big.multiply(big1));
System.out.println(big.divide(big1));
}
}
BigDecimal类
概念
不可变的、任意精度的有符号十进制数
常用方法
1.不可变的、任意精度的有符号十进制数
2.构造方法:
① BigDecimal(String val)
3.常用方法:
① 加 add(BigDecimal augend)
② 减 subtract(BigDecimal subtrahend)
③ 乘 multiply(BigDecimal multiplicand)
④ 除 divide(BigDecimal divisor, int scale, int roundingMode)
注意:
第二个参数表示小数点保留位数
第三个参数表示舍入模式 :
Round_HALF_UP 四舍五入
代码
package com.demo;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
public class BigDecimal类 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BigDecimal big = new BigDecimal(12.3);
BigDecimal big1 = new BigDecimal(12.3f);
BigDecimal big2 = new BigDecimal("0.35");
BigDecimal big3 = new BigDecimal("1");
/* System.out.println(big);
System.out.println(big1);
System.out.println(big2);*/
//运算/*System.out.println(big2.add(big3));
System.out.println(big2.subtract(big3));
System.out.println(big2.multiply(big3));*/
System.out.println(big2.divide(big3,1,BigDecimal.ROUND_HALF_UP));
}
}
时间类
Date
java.util 表示特定的瞬间,精确到毫秒
1.构造方法:
① Date()
1> CST : 美国中部标准时间: 美国、澳大利亚、古巴或中国的标准时间。
② Date(long date) 根据参数的毫秒值换算时间 从历元1970年1月1日0时0分0秒开始算。
2.常用方法:
① getTime() 返回对象到历元的毫秒值
代码
package com.demo;
import java.util.Date;
public class Date类 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Date date = new Date();
// System.out.println(date.toGMTString());
Date date1 = new Date(1000);
// System.out.println(date1.toLocaleString());
// System.out.println(date.getTime());
// System.out.println(date1.getTime());
// System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis());
}
}
Calendar类
1.Calendar:日历类:抽象类
2.创建对象:
getInstance()
3.常用方法:
①get(int field)获取字段对应的值
② add(int field, int amount) 设置日历的方法,添加或减少
注意:
通过 正数 、 负数来表示加或减
③set(int field, int value)设置
代码
package com.demo;
import java.util.Calendar;
public class Calendar类 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建对象
Calendar cd = Calendar.getInstance();
/*System.out.println(cd.get(Calendar.YEAR));
//西方第一个月份为0 ,值需要加1
System.out.println(cd.get(Calendar.MONTH)+1);
System.out.println(cd.get(Calendar.DATE));
System.out.println(cd.get(Calendar.HOUR_OF_DAY));
System.out.println(cd.get(Calendar.MINUTE));
System.out.println(cd.get(Calendar.SECOND));
//西方从周日开始 值要减 1
System.out.println(cd.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_WEEK)-1);*/
//设置日历的方法
cd.add(Calendar.MONTH, 13);
System.out.println(cd.get(Calendar.MONTH));
}
}
SimpleDateFormat 时间日期格式化类
1.格式化 : 日期 –》 字符串
2.解析 : 字符串 –》 日期
3.DateFormat :抽象类:
子类:SimpleDateFormat
4.常用方法:
① 格式化 :format(Date date)
② 解析: parse(String source)
5.构造方法:
① SimpleDateFormat() 使用默认模式进行格式化或解析
② SimpleDateFormat(String pattern) 使用指定模式
常见模式:
y 年
M 月
d 日期
H 0-23
m 分钟
s 秒
E 星期
代码
package com.demo;
import java.text.ParseException;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
public class 日期格式化类 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ParseException {
SimpleDateFormat sf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy年MM月dd HH:mm:ss E");
/* Date date = new Date();
String value = sf.format(date);
System.out.println(value);*/
//2021年11月02 17:17:56 星期二
Date date1 = sf.parse("2021年11月02 17:17:56 星期二");
System.out.println(date1);
}
}
数字格式化类
概述
NumberFormat 数字格式化类 该类是一个抽象类
1.构造方法:
① getInstance() 返回当前默认语言环境的通用数值格式
② getCurrencyInstance() 返回当前默认语言环境的货币格式
③getPercentInstance()返回当前默认语言环境的百分比格式
2.常用方法:
① format(double number) 格式化
② setMaximumFractionDigits(int newValue) 小数部分允许最大位数
③ setMinimumFractionDigits(int newValue) 小数部分允许的最少位数。
④ setMaximumIntegerDigits(int newValue) 设置整数的最大位数
代码
package com.demo;
import java.text.NumberFormat;
public class 数字格式化类 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
NumberFormat nf = NumberFormat.getInstance();
// NumberFormat nf = NumberFormat.getCurrencyInstance();
// NumberFormat nf = NumberFormat.getPercentInstance();
// nf.setMaximumFractionDigits(5);
// nf.setMinimumFractionDigits(3);
// nf.setMaximumIntegerDigits(3);
System.out.println(nf.format(12345678.6));
}
}
DecimalFormat类
1.DecimalFormat:用于格式化十进制数字
2.构造方法:
DecimalFormat(String pattern)
注意:
# 小数位数不够不补0
0 小数位数不够 补0。
代码
package com.demo;
import java.text.DecimalFormat;
public class DecimalFormat类 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// DecimalFormat df = new DecimalFormat("##,##.##");
DecimalFormat df = new DecimalFormat("00,00.00");
System.out.println(df.format(12345678.1));
}
}